You start with a 3x3 square of nine cells
Each player (in their turn) puts their "X" (first player) or "O" (second player) in a cell.
The game is over when there are three Xs or three Os in a row, column, or diagonal.
RoadMap: You begin today programming in Java, which is a real programming language used by real programmers in the real world. Java is very picky about how you spell things, so you will begin by translating four programs already known to work, so you can concentrate on the Java syntax (spelling). When you finish them you can do some bigger projects, initially some of the same programs with full graphics. Then you will be ready to write anything you want. You can do this, but it will take time. Stay with us and we will get you there.
This is the second part of a self-paced short course designed to
get eager, self-motivated people started in the skill of programming.
The first part discusses program structure in a language-neutral way, using
a subset of English. Nobody learns programming in one or two weeks or even
a whole semester, it takes time and practice -- "motivation and miles"
-- but we can give you a roadmap. Once you more or less understand the
basic structure of things, you can look at existing programs and figure
out how they work -- and by extension and a lot of copying, you can write
your own code to do similar things.
Most of this page explains how to translate a program written in what we call "Kitchen English" into an equivalent program in Java, which runs pretty much exactly the same. It is important thaat you translate each English line exactly, so that you will understand what the Java parts do. Later, when you are writing your own programs, you can get creative, because then you will already know what the parts do.
Here are the topics we cover, which you may want to come back and review if you get stuck later on:
Top-Down Design
Design in English
Six Ideas in Java
Sequence
Iteration
Conditionals
Boolean Operators
Variables
Scope
Input/Output
Simple Input
Subroutines
Strong TypesTranslation Summary (Quick Reference)
Errors & Fixes (Quick Reference)
Computer programming -- at least what they call "programming"
(a lot of computers are programmed in other ways, but nobody wants to admit
that's what is happening) -- is mostly text-based, so I had a lot of text
to explain that, but nobody wanted to read it. I still rather like what
I said, and you can read it here (it won't cost
you much, but it does help you know if this is what you want to do for the
rest of your life).
This story is how to play Tic-Tac-Toe.or perhaps better:
This story is how two people (or one person against the computer) play Tic-Tac-Toe.
Then, indented under that line, you break that one sentence description
into two or three (not more) short (one line) descriptions of the biggest
chunks of that whole program, so that the three sentences add up to the
same thing that the top line says.
This story is how two people (or one person against the computer) play Tic-Tac-Toe.
You start with a 3x3 square of nine cells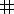
Each player (in their turn) puts their "X" (first player) or "O" (second player) in a cell.
The game is over when there are three Xs or three Os in a row, column, or diagonal.
Then you do the same thing again for each of those new lines.
This story is how two people (or one person against the computer) play Tic-Tac-Toe.Eventually you get to the level of detail where each line is one of the Six Ideas. That is your program (in English, see below).
You start with a 3x3 square of nine cells 
You draw two vertical lines across two horizontal lines.
You can number them 1..9 across the top and down to the bottom.Each (in turn) puts their "X" (first player) or "O" (second player) in a cell.
The human player types in a number to play that cell.
The computer scores each possible cell, then plays the highest score.The game ends when there are 3 Xs or 3 Os in a row, column, or diagonal.
...
In the following descriptions, "statement" is a single command, either a subroutine call or variable assignment, or else a complete iteration or conditional. In the code examples it is written in italics "statement" to show that any statement can be there. Italics also are used as place-holders for arbitrary expressions or names supplied by programmer. Reserved words (not allowed as variable or subroutine names) are shown in bold. Other actual code is shown in typewriter font. Colors are used to show relationships
Comments are not part of the program that the computer runs, they are only there to help people (you and your colleagues) read and understand the code. A comment either starts with two slant characters "//" and ends at the end of that line, or else (called "block comment" because it can extend over several lines) starts with "/*" and ends with "*/". I often use comments here to explain the example code.
You will see examples of these Java statement
types as we go along, sometimes before they are explained, so you should
read this whole page straight through in one sitting, then come back and
read each section more carefully. Then when they are needed in the code
you write, come back and read it again. Don't worry too much if the explanation
here is obscure on the first pass, after looking at the examples three
or four times it should start to make sense. If not, that's my fault, not
yours, ask for help, and the next student trying to understand
this will have a better shot at it -- because when you ask for help, the
documentation gets better. Really. We need your help to make it
better ![]()
Sequence in Java is spelled with a semicolon ";" which terminates each subroutine call or variable assignment or declaration (statement), or else with a pair of braces "{...}" that combines into one statement a whole sequence of statements.{;;; {}} // four null statements (they do nothing) combined into one statementIn English, each line is one statement, but in Java whatever ends with a semicolon is one statement. It is customary in Java to put one statement on each line (if it fits) and indent any spillover into the next line, because that makes it easier to read. Some C programmers consider it great sport to put their whole program on one line (some compilers have line length limits, which makes packing it in interesting), but of course that takes a lot of time (and time is money), so you should not try to do that with real programs.In English you can terminate the sequential execution of the program with the Stop command. In Java it's a system subroutine call:
System.exit(0);
Iteration in Java comes in several forms, but only two are really useful:
while (expression) statement
// the expression should evaluate to true or falseThe expression is tested before the loop statement executes each time through, and any time it is false the loop terminates (and proceeds with the next statement after the loop) without doing statement at allThe statement is whatever you want repeated. Most programmers always wrap braces {...} around the statement so they don't need to think about adding them if they later decide to add another statement inside the loop.
for (name=expression; expression; statement) statementname is a variable, declared either here or previouslyThe for-loop parentheses and the semicolons are required, but the expressions and statements between them are optional (I do not recommend leaving them out, it makes your program hard to read). The assignment, if omitted, could be replaced by some other initialization in a prior line. The second expression, if omitted, is assumed to be true (it would be a never-ending infinite loop unless you have an explicit break inside)The first expression is an initial value given to that variable
The second expression is a boolean value, usually testing name against some end value, and works like the expression in while
The first statement is typically an increment or decrement on the variable, which executes after the end of the second statement
The second statement is whatever you want repeated.
For example, this is exactly equivalent to the corresponding while-loop above:Important: The semicolon that ends an iteration is the semicolon at the end of the statement (there is no extra semicolon after the right parenthesis; if you put one there, then the statement part won't be iterated at all.for (; expression;) statementTwo other commands inside the statement give more precise control of the loop operation:
break; // immediately exits the loopcontinue; /* immediately skips to the loop's next iteration, including any incrementation statement and the test expression*/
Examples: In English there was only one form of iteration, the Repeat, for example:Repeat 3which prints "Hello" on three successive lines. In Java that would look like this:
Print "Hello"
Nextfor (int n=0; n<3; n++) System.out.println("Hello");In English, if we wanted to do something that counted the iterations and numbered the steps, we would need to declare a separate variable, but that variable is built into the Java for-loop (n in our example above). Here we want to show our count, first in English:Variable n = 0Here's the same thing in Java:
Repeat
Add 1 to n
If n>9 then Exit
Print n # ".."
Nextfor (int n=1; n<=9; n++) System.out.println("" + n + "..");
or alternatively:int n = 0;
while (true) {
n++;
if (n>9) break;
System.out.println("" + n + "..");}
Notice that the concatenation operator in Java is the same as the addition operator (that's called "operator overloading" in C where the programmers are encouraged to do stupid things like that) so if you don't make sure the value on its left is a String (of characters, in this case the empty string ""), it will attempt to do arithmetic and get wrong results, and the compiler won't help you. I think that was a mistake but they didn't ask my opinion, so you are stuck with the result. It is what it is.
Conditionals come in two flavors in Java, but we will mostly only use the familiar if..else:
if (expression) statement else statementThe expression is a boolean value, which if it evaluated true, the first statement is executed, otherwise the second statement is executedThe else-part (with its statement) is optional. Most programmers always wrap braces {...} around the statements, so they don't need to think about adding them if they decide to add another statement under the control of the condition.
After you are more comfortable writing Java code, you can read about the other kind of conditional in the Switch section of the "Things You Need to Know in Java" page.Examples: The English conditional only let you control one statement. Technically that's true also in Java, but everybody uses braces without even thinking about it. You could do that in the Kitchen English programming language too (using an iteration) but it was unobvious:
Input YourGuess
If YourGuess = MyNumber then Repeat 1
Print "You got it!"
Add 1 to wins
Next
In Java that might look like this (using my "safe" input):int YourGuess = Zystem.ReadInt();
if (YourGuess == MyNumber) {
System.out.println("You got it!");
wins++;}
The Kitchen English programming language only lets you compare for equal, less, or greater; Java also lets you compare for their negations:
Op True Negation Equal == != Less < >= Greater > <=
Notice also that to test if a value is equal in Java uses a different symbol '==' than making it equal in an assignment '='. They really are different things, but because they use separate symbols, the Java compiler can (and does!) also let you do assignments in places where they don't belong -- and the Java compiler will not always warn you! For example,boolean A = true, B = false;
if (A=B) System.out.println("Equal!");
This will actually compile and run in Java (and print "Equal!"). Java repaired a lot of C's mistakes, but this wasn't one of them. If A and B are numbers, then the compiler will complain, not that you set them equal (which is the real bug) but that it's expecting a boolean value inside the parentheses. It is what it is. You can't always trust the error message, only that there's some kind of programming error on (or before) the line where it complains. If you can't find it, get help from somebody who has more experience. Or if you compile often (which is a good idea) you can look for your error among your most recent changes.String Compare
The Java designers chose to make String an Object type rather than a primitive value type, which makes it rather more awkward to work with. That's unfortunate, because it is used everywhere, and should be easy. It is what it is. We will get to the complexities of Objects much later (or you can read about "Objects and Classes" in the "Need to Know" page), but we need String values now. What you don't need to know is that you can compare Objects for equality (it's the same object or not) but ordering makes no sense. String values are the other way around: two different String Objects might have the same sequence of characters internally, and there is no useful reason to know that they are not the same Object, and always we want to know if the characters are the same, or if one is alphabetically greater or less than the other. That should be as simple a a compare operator, but Java got it wrong. Instead you must remember to call an object method: For Englishif varA > "abc" then somethingyou need to write in Java:if (varA.compareTo("abc")>0) something;It's worse if you try to compare two String variables for equality and forget to use the subroutine call. The Java compiler accepts this as valid Java code, nevermind that it may fail to do your something when the underlying string values are in fact equal:if (varA == varB) something;
Combining Boolean Comparisons
The Kitchen English programming language has no way to combine boolean values in a single expression. Sometimes programmers need to do that, but usually in large complicated programs, which you have not seen so far. In spoken English you might say "if the truck is blue AND the car is red then..." but you can also say "if the truck is blue then if the car is red then..." to get the same effect, and it works in Kitchen English. There are several ways to combine these two conditions, as shown in this diagram, where the top half represents the blue truck and the bottom half is some other color of truck, andthe left half represents the red car and the right half is some other color of car:If both are true, then you get the top left quadrant ("AND" which is '&&' in Java). If neither is true, you get the bottom right quadrant. You might want the condition where either the truck is blue OR the car is red (or both), which is every possibility except the bottom right. You cannot say that in Kitchen English directly, you must make up a combination like this:Let either = falseIn Java you can do that, but usually you use the boolean OR operator '||':
If the truck is blue then Let either = true
If the car is red then Let either = true
If either is true then ...if ((truck == blue)||(car == red)) {...Note that the extra parentheses are required, Java got the operator hierarchy wrong for what everybody needs these operators for. Other combinations you can make up with the NOT operator ('!' in Java), for example any of these three are the same bottom right quadrant:if ((truck != blue)&&(car != red)) {...Again, you need the extra parentheses. Extra parentheses never hurt (except too many of them make it hard for people to read).
if (!((truck == blue)||(car == red))) {...
if ((!(truck == blue))&&(!(car == red))) {...
Variables (sometimes also called "fields") must always be declared to be a particular type in Java before they are used, and may optionally be given an initial value in the declaration. Multiple variables may be declared of the same type in one statement (ending in a semicolon), but you cannot declare the same variable name multiple times (in the same scope, see below). The type must be a previously defined class name (see "Objects and Classes" in the "Need to Know" page because we mostly won't get there), or else a defined scalar type like boolean, char, int, float or double. The last three are numbers, and if you mix different sizes of any number type, Java will promote the operation to the highest precision (typically double). That's reasonable. What is unreasonable (and it will bite you because the compiler should complain, but it doesn't) is that Java considers characters to be compatible with numbers, and gives you no warning if (for example) you try to compare a character to an integer, like this:
int num = 3;The numeric value Java sees in variable ach as 51, not 3, so of course comparing them is never equal. This is a blunder, but they didn't ask my opinion. You need to be careful when working with characters.
char ach = '3';
if (ach == num) ThisSubroutineNotCalled();Notice that Java allows only one type for each variable, and every value you want to put into a variable must be the same type as the variable. The types must match (or at least be compatible, that is, Java knows how to convert them). The English computer automatically did whatever conversion was necessary.
Here is an example of two variable declarations, the second being the system-defined String type:
int abc, xyz = 0, aHugeVeryBigName = xyz+8;
String aWord = "Mary";Variables can be given values when they are declared, and/or elsewhere in the program like this:
abc = aHugeVeryBigName-xyz+33;Notice that only one line tells Java the type (in this case int); if you try to use the type name on multiple lines that set a new value to abc, Java will be confused and refuse to run it. You can give the same value to multiple variables in a single command, but I don't encourage it (look it up online if you want to do that). Start simple, you can get tricky later (tricky is not a good idea, but some programmers consider it fun; the manager paying you to write a program usually has a different opinion).The familiar arithmetic operators (+ - * /) work on the number types in Java, along with various bit operators you mostly don't need in the programs we are doing here, and you can group operations using parentheses, where the subexpressions inside parentheses are evaluated before being combined with any operations outside. Everything else is done by subroutine ("function" or "method") calls.
You also have easy ways to add (or subtract) 1 to a variable:
n++; // is the same as (English) 'Add 1 to n'There are update forms for most of the operators, but you can learn them later (if you so choose; me, I don't use them at all because they are only more things to know and be concerned about, but offer no advantage).
n--; // is the same as (English) 'Subtract 1 from n'Scope: In English all variables are global, that is, you can declare a variable anywhere in your program and use it anywhere else, and it's the same variable everywhere. In Java a variable is only visible inside the most nearly enclosing braces, called its scope (that's Greek for "visible"). I recommend that variables used only inside a single subroutine be declared at the beginning of that subroutine, just inside the left brace (see examples below), but if you want the same variable to be used in several subroutines, or if you want to preserve its value between subroutine calls, you must declare it inside the outer braces of your compiled class (see examples below). Until we start using the "Object-Oriented" (OOPS) features of Java, all the variables you declare at the class level (only) need the magic word "static" in front of the type name.
The first four programs you write in Java, you will use the simple rules described on this page to convert (translate) your English code to Java, line by line (except you should move all variable declarations out to the class level), and it will work. See also the Translation Summary where all this is collected together in a single table. After you get each program working in Java, you should go back and decide which of these variables should be parameters, and which should be local, so the Java code looks better and is easier to understand.
Java allows variables to be declared anywhere in your program, but the variables declared inside a subroutine can only be used inside the nearest brace pair, and only after they are declared. I do not recommend it, but many Java programmers declare for-loop control variables inside the parentheses of the for-loop (see the first for-loop example above). Java could and should prevent you from accidentally re-using a control variable, but this habit at least prevents one of the possible bugs that people might make.
Examples: If you have the same variable name declared at different scopes (levels), only the nearest (by counting braces) declaration will be used. So you could (this would be A Very Bad Idea) do something foolish like this:
class MyClass {
static String x = " Hello"; // visible everywhere inside MyClassstatic void fust() {
char x = '?'; // hides outer String x
for (int x=1; x<=9; x++) { // hides outer char x
System.out.print(x);} // prints digits from 1 to 9 on a line
System.out.print(x);} // adds a question mark to the linestatic void main() {
fust(); // prints '123456789?'
System.out.print(x);} // prints ' Hello' on the same line
}
So here you have three identical print statements in the same program printing the same variable name x but printing very different things from three separate variables, with no confusion -- except in the mind of the programmer trying to understand what is going on. Don't be that person.But you certainly need to declare some variables at the class level (they are called class variables or fields) so you can preserve their values across multiple subroutine calls, and other variables inside their respective subroutines (they are called local variables) so you don't need to worry about accidentally using the same name in another subroutine the next week. When you have values used in a single subroutine but prepared outside where it is called, you should use parameters (see examples in "Subroutines" below); when a subroutine calculates a single value for the use of its caller, you should return it as a function result.
Input/Output in Java is always by predefined subroutine calls.
The Output you will use most often in Java is the (console) print command -- I mean subroutine, ah, "method" -- for displaying text. It's the same as the English Print command, except for the spelling. Basically, the English
Print "Hello"is spelled in Java:System.out.println("Hello");I need to say some more about this because English is so forgiving and Java is not. The Java subroutine (see "Subroutines" below) takes one parameter which is a String (see variable types above). When you and I want to use this command in real programs, we usually have a collection of values (most often numbers, which are a different type in Java) that we want printed, mostly so we can figure out why the program isn't working right. What we need to do -- and what you need to become so familiar with that it's second nature to you -- is to turn that collection of numbers and other values into a single String value for the subroutine to print.The key insight is that a String value "plus" (that is, using the '+' symbol in your code) any other value becomes a longer string with that number (or whatever) converted to text and concatenated onto the previous string. For example, the string constant "Hello" + aNum (where aNum is declared as an integer variable and has the value 123) is understood by Java as having the value "Hello123". This then can be the left-hand string to which you append ("+" but it's concatenation, not addition) other values.
Mostly you are using this in your program where you have previously calculated values for variables like aNum and xValu, and you have some line of code that is supposed to compute the value of myRez from those two variables, but the answer in myRez doesn't behave like you think it should. This happens all the time, so pay attention. You insert a new line after the calculation (or before it if either aNum or xValu is altered in the computation),
System.out.println("BadCalc " + aNum + ", " + xValu + " => " + myRez);The idea here is that all the values you want to look at (in this case aNum and xValu and myRez) are connected together with a bunch of quoted String constants (typically spaces) so you can see where one value ends and the next begins in the printout. The aggregate must always begin with a String, so I always try to put something unique there, like a descriptor of what I'm looking for or where the line is, something that visually looks different from every other print command in the whole program. If any of the values are String or char variables that might be empty or have spaces in them, I make sure the spacing constants also have apostrophes or back-quote characters so I can see where the data begins and ends, like thisSystem.out.println("Str+char '" + aStr + "' `" + xCh + "`");Don't forget the plusses -- well, if you do, the compiler will remind you, but -- better you know enough Java that putting the plusses in comes naturally. Also don't forget to start with a string, otherwise the plusses will add instead of concatenating. It's a stupid rule, but it's what we must live with (it's in C++ too, so learn it).After you have all these print commands all over your program, and after the program is running correctly, then you probably want to remove them. Me, I'm lazy -- especially if I'm still making changes and things might break (they always do) and I might need those print lines again -- so I declare a single boolean constant at the front of the class:
final boolean noisy = true;then in front of all those debugging print lines,if (noisy) System.out.println("whatever..."Then to see how it looks without all those debugging lines, I just turn the boolean offfinal boolean noisy = false;and all the print lines suddenly do nothing.Examples: In English we had Print and Input commands for text I/O. The Java subroutines to do these simple things are more complicated than they need to be, but you can think of them as "silly long names with dots in them" for now. The dots have to do with classes and objects, which we will get to much later (you can read about them in the "Objects and Classes" section of the "Need to Know" page). So, the English
Print "Hello"is spelled in Java:System.out.println("Hello");
You also can print multiple things on the same line:System.out.print("Hello,"); System.out.print("World!");which prints 'Hello,World!' on the one line. In English you could do it this way:Let Hello = "Hello,"
Print Hello # "World!"
In English you can specify what kind of input you want using a number after the variable name on the Input command line:Input word {gets whatever the user types, up to but not including Enter}
Input number,-1 {gets only a number, all else ignored}
Input letter,1 {gets a single (capitalized) character}
Java has very complicated ways to do the same kinds of input but I wrote some simplified input routines in a special "Zystem" class (see "Input Routines in my class Zystem" in the "Things You Need to Know in Java" page), which you can use for now:String word = Zystem.ReadWord(); // same as EnglishNotice that Java allows only one type for each variable (in these three lines, String, then integer, then character). If you open up the Zystem file you can see that those three input routines are declared to return those three types. The types must match (or at least be compatible, that is, Java knows how to convert them). The English computer always did whatever conversion was necessary.
int number = Zystem.ReadInt(); // ignores spaces but stops at non-digit
char letter = Zystem.ReadLetter(); // one (including Enter) uncap'dZystem.ReadLetter() works differently from the English Input command because the Java run-time requires a carriage return (Enter key) at the end of every input before the Java program sees anything. Sometimes your program needs to see that line-end, sometimes not, so it becomes your responsibility to throw it away if you don't want it. Assuming you have declared variable char letter somewhere in your program before your input, you can use a while loop like this to discard everything that isn't printable text:
while (true) {If you look in the ASCII Table in the "Need to Know" page, you can see the character ordering of the first 128 UniCode characters, that control characters like the Enter and Backspace and Tab keys are all earlier in the table than the space bar, and all the normal alphabet are after it. The numbers and letters are in sequential order to make it easy to compare things like that.
letter = Zystem.ReadLetter();
if (letter > ' ') break;}Also, the English Input command capitalized the letters that came in but Zystem.ReadLetter() does not. You can depend on the ASCII order to do that yourself in a couple lines;
if (letter >= 'a') if (letter <= 'z')In Java this might work without the type-casting (using "(int)" to tell the compiler to treat this value as if it were an integer, and then "(char)" to tell the compiler to treat the computed value as a character again), but I wouldn't trust it, nor my memory to remember I'm doing type-unsafe things here, next time I look at the code. Use the ASCII chart to convince yourself that subtracting 32 gets to the capitals, or else step through this in the debugger to see it happen.
letter = (char)(((int)letter)-32);
Subroutines in Java are called "methods" for no particular reason, and can be declared only inside class definitions. They have an optional return type, a name, and a parameter list of zero or more typed parameters that look more or less like variable declarations separated by commas rather than semicolons and enclosed in a pair of parentheses. The parentheses are required, both in the declaration (sometimes called the "header"), and also every place the subroutine is called, even if there are no parameters. The body of the method is enclosed in a pair of required braces. If the subroutine ("function") returns a value, it must end in a return statement giving the value to be returned, which must be the declared type and ending in a semicolon; otherwise the declared type is void. Here is the general form:
static typename(parameter list) {The gray "static" you should always use until you get into OOPS (after you complete Seaman in Java). It means this subroutine is not "Object-oriented." The gray "return value;" is required when the type is an ordinary type name (not void), and the value must be that type. All Java subroutines or functions must be declared inside a class declaration and not inside another subroutine or function.
// subroutine body here
return value;} // end of nameIn English, all the subroutines have no parameters and no return value, so when you translate your English code to Java, all the methods (subroutines) will look like this:
static void mySubroutine() {Later, after you get the hang of it, we will talk about appropriate parameters and return types.
...
} // end of mySubroutineHere are two specific examples (there are others below). Note that the first example has a single integer parameter, and the second example here is a function with no parameters and requires a boolean result (in this case the constant value true):
static void mySubroutine(int z) { // one parameter z
System.out.println("z = " + z);
} // end of mySubroutine
static boolean myFunction() { // no parameters
System.out.println("in myFunction");
return true;} // end of myFunction
When you call a subroutine from somewhere else in your program, it looks maybe like this:if (myFunction()) // the boolean result controls the conditional
mySubroutine(7); // no result to use
else mySubroutine(0);
You need to be careful that your argument values in the call statement line up properly with the parameters (same number, same order) in the subroutine header. Any subroutine or function may return early with a return statement giving the value, or if void, the return statement alone, in either case always ending in a semicolon.Here is an example of a trivial method (function) returning the sum of its two parameters:
static int sum(int a, int b) {return a+b;}
...
int five = sum(2,3); // arguments: 2,3 match params a=2, b=3
Classes in Java are a way to group related data and methods into a separate compilation, where the class name becomes a new data type with its own copies of the data declared in the class. Most of the programs you will write in this curriculum are not object-oriented, so we will introduce those distinctives when we get there, (see "Objects and Classes" in the "Need to Know" page because we mostly won't get there).Examples: The Real World is not "object oriented" so of course the English language isn't either, and we knew nothing of classes and objects when we wrote programs in the "Kitchen English" programming language. But we did have subroutines, which were declared with a name in quotation marks, and were called by the same name without the quotes. For example, if we have in English:
Variable x = 23
Do times6
Do my Subroutine
Add 3 to x
Do my Subroutine"my Subroutine"
Print "x = " x
Done"times6"
Let x = x*6
Done
The same thing in Java looks like this:class Example {
static void mySubroutine(int z) {
System.out.println("x = " + z);
} // end of mySubroutinestatic int times6(int y) {
int rez = y*6;
return rez;
} // end of times6static void main() {
int x = 23;
x = times6(x);
mySubroutine(x);
x = x+3;
mySubroutine(x);
} // end of main
} // end of Example
Notice first that English allows spaces in the subroutine name, but Java does not. You can just delete the spaces and change the next letter to a capital for readability, or you can use the underscore character (shift-hyphen "_") which is considered to be a letter in Java but not allowed in English.Notice that x declared inside main is copied to parameters y and z when calling those respective subroutines. All English variables (including subroutine parameters and results) are global, so you just set the values then called your subroutine, then got the results when it got back. In Java you can declare variables inside any pair of braces (the for-loop parentheses are presumed to be inside its braces, even though they really aren't) and those variables are visible only inside those braces -- sometimes, but not always, only after the declaration, so it's a good policy to declare variables always before they are used. See the nested variable example above for how that works.
Every Java program is expected to have one subroutine named "main" which is also static -- which means it exists outside the class; static subroutines can only refer to static class variables and subroutines; for now everything is static at the class level, but later, when you do real objects, that won't be necessary. From the Bad Olde Unix dayes, the main subroutine is often expected to take an array of String values (you will always see an example of what this looks like when you come to a new IDE), but modern point-and-click implementations don't pass any command-line parameters. You should be prepared for either kind. Your program is always started by the operating system calling its main() subroutine, which then does whatever your program needs to do.
The next thing to do is to add Java subroutine headers to match the English subroutine structure. If you did your program Design using our Design Tool, this can be as easy as clicking the Java radio button and Updating it, then some copying and pasting.
Third, you need to go through your English code and identify all the variables that are used in more than one subroutine, and make declarations for them at the class level (before your first subroutine). The Design Tool should help you with this, especially if you kept it updated as you added variables. You need Java declarations for all variables, including the ones you did not move out to the class level. The variables that you did move out, if they were initialized in the subroutine, you may need an assignment statement (but not a declaration) there in the Java to preserve setting that initial value. That takes careful analysis, what this variable is used for, and where it is being set.
Finally, go through the code again, adding Java code to match the English code (in the comments). The following table of conversions can be helpful when you are getting started. Click and bookmark this PermaLink so you can come back here as needed.
| How Do I...? | English | Java |
| Add two variables (put sum in a variable) |
Let sum = varA+varB | sum = varA+varB; |
| Add +1 to a variable | Add 1 to varA | varA++; |
| Add +2 to a variable | Add 2 to varA | varA = varA+2; |
| Array access, nth item of naryA | ... item n of naryA ... | ... naryA[n] ... |
| Call subroutine xxx | Do xxx | xxx(); |
| Comment | {Comment} | // Comment |
| Declare and initialize an integer variable | Variable varA = 0 | int varA = 0; |
| Declare and initialize a character variable | Variable varC = ' ' | char varC = ' '; |
| Declare uninitialized word variable | Variable varW | String varW; |
| Declare an uninitialized character array (length 40) | List varA | char[] varA = new char[40]; |
| Input single letter | Input varA,1 | while (true) { varA = Zystem.ReadLetter(); if (varA > ' ') break;} |
| If condition is true, do something | If condition then something | if (condition) something; |
| {English has three compares...} | if valueA = valueB then something | if (valueA == valueB) something; |
| {...Less...} | if valueA < valueB then something | if (valueA < valueB) something; |
| {...and Greater...} | if valueA > valueB then something | if (valueA > valueB) something; |
| Java does not compare String values | if varA > "abc" then something | if (varA.compareTo("abc")>0)
something; |
| One condition, do 3 things | If condition Repeat 1
somethingA somethingB somethingC Next |
if (condition) {
somethingA; somethingB; somethingC; } |
| Print label and variable | Print "label" # variable | System.out.println("label" + variable); |
| Print 5 items in an array length 5 | Print arrayA | for (int n=0; n<5; n++)
System.out.print(arrayA[n]); |
| Repeat something 3 times | Repeat 3 something Next |
for (int n=0; n<3; n++) {
something; } |
| Repeat something until condition | Repeat if condition then Exit something Next |
while (true) { if (condition) break; something; } |
| Restart Repeat at top | if condition then Again | if (condition) continue; |
| Terminte the program | Stop | System.exit(0); |
You need to be rather more careful with your alphabetic constants in Java than was necessary in English. A Java String of (zero or more) characters (type char) is quoted by the double-quote character, and individual characters are quoted by a single-quote (on most keyboards it's the same key, but unshifted). The compiler will complain, but their error messages don't always make sense. Examples:
char x = "x"; // error, should be 'x'
String z = 'z'; // error, should be "z"
System.out.println('Hello'); // error, should be "Hello"
System.out.println('I'); // might error,
// better: println(""+'I') or println("I")
The essence of strong data types is that you must declare the type (tell the compiler your intentions) of anything that can have a type before you ever try to use it, and then the compiler will refuse to accept it if you accidentally try to do something inappropriate. Very large programs -- think: thousands or millions of lines of code -- nobody can keep all that logic in mind at once, so we need all the help we can get from the compiler. The strong type system is your friend, be nice to it.
In the following projects you will be converting the four programs you wrote in English into Java. English is untyped (OK as a learning tool, but rotten for heavy lifting), so an important part of converting them to Java is choosing an appropriate data type for each variable. This will be covered in the discussion.
Subroutines (in Java they are called methods or functions) have several places where the strong type system is exercised. Let's review them here. Here is a subroutine like many you will see (and write!) in Java:
static void main() {The first line is called the "method header" and it declares everything we need to know about this subroutine. It also happens to be the correct form for the main program in any Java program (except in Unix environments like Replit you need a parameter that nobody ever uses: just copy the example when you get there).
int x = 23;
/// ... (more code here)
} // end of main
The first word "static" means this subroutine is not "object-oriented" (OOPS, see "Objects and Classes" in the page on "Things You Need to Know in Java"). Java is intended to be OOPS, so everything else -- including the required "main" routine -- must be specially marked as not. What can I say? They didn't get everything right, but they tried, and they are way ahead of whatever is in second place. You need to put "static" in front of every method header you write in this course, until you get to the OOPS part. The compiler will complain if you don't, but copy-and-paste is easy.
The second word "void" is a magic word that means "not a data type". Subroutines can return a single value -- we call them "functions" when they do -- but if not, we need to tell the compiler that we don't want a return value. The word void goes in the place on that line that the return data type would go if a value is returned. We'll get to that shortly (below).
The third word "main" is the name of the routine, and the empty parentheses "()" tells the compiler that this is a subroutine and there are no parameters. Always we need to tell the compiler what our intentions are.
The next line is the beginning of the subroutine body, and it declares a local variable "x" and gives it an initial value 23. The variable x is visible only between the opening brace in the header and the closing brace at the routine end. That way you can have thousands of subroutines in your program, and many of them can declare local variables named "x" and there is no confusion. Also this variable must have a type (in this case integer) spelled "int" which means this variable can only have integer values. The compiler will complain if you deviate from this stated intention. See also "Variables" above.
Here is another subroutine (called a "function" because it returns a value), which you also already saw above:
int sum(int a, int b) {If you decided to test this subroutine in the Hello class in the next section, you would need to add a "static" in front because you have no way to call it in an object-oriented way yet.
return a+b;
} // end of sum
We know this subroutine is a function because it is declared with a type name "int" and not "void". That also means that a "return" command is required for every possible path through the function, and it must be an integer value in each case. For example, if you changed the return line to be conditional:
if (a>0) return "a+b";the compiler would complain for two reasons, first because you are trying to return a string (which is not an integer), and then again because if the parameter value a is zero or less, it would be possible for execution to get to the end brace (on the third line) without executing any return at all.
Continuing with our analysis of the header line, we see two parameters, both integers. Parameters are essentially local variable declarations, which are initialized with values provided by the calling code, so they must always be given a data type. When the subroutine is called, the compiler verifies that that the values supplied are compatible with (can be automatically converted to) the declared types. Integers are pretty restrictive, you can automatically convert a character (type "char") to it -- I think that is a mistake, but they didn't ask my opinion -- but not much else. Anything else, you need to do the conversion yourself (that would be a good thing, you don't want stuff like that happening by accident). As noted above, integers can be automatically promoted to float or double, but (surprisingly, because it is allowed other places) not to String. Whatever. Best you do explicit conversion every place you want it.
That should be enough to get you started. We'll try to remind you as we go along. See also "Variables" above for other ways that strong types are different from untyped languages like English. You should also read through our discussion on Subroutine Parameters at least once, and maybe also the first few times you are laying out the data for a new program.
If you came here from some other part of the tutorial to review data types, you can use your browser's GoBack button to return. Otherwise...
OK, let's get started.
Next: Programming Environment.
<<Previous | ToC | Next>>
2023 May 11